A home addition is a big investment, and getting the financing right can make or break your project. The last thing you want is unexpected costs or loan terms that don’t work in your favor. That’s why planning ahead and choosing the right financing option is just as important as picking the right contractor.
According to Advance Design Studio, Americans are projected to spend over $1.2 trillion on home renovations in 2025, fueled by a combination of economic factors, evolving lifestyle needs, and a growing desire for personalized, sustainable spaces.
At Seanote Construction, we believe in honesty over empty promises. If something doesn’t make sense financially, we’ll say so. If a budget doesn’t match the scope of work, we’ll break it down clearly. We’re transparent about pricing, we stand by our work, and if something goes wrong, we fix it.
Key Takeaways
- Budget for materials, labor, permits, and unexpected costs to avoid financial surprises.
- A strong credit score and home equity improve your chances of getting better loan terms.
- Compare loan types like HELOCs, refinancing, and construction loans to find the best fit.
- Always get the required permits and follow local codes to prevent delays or fines.
What Is a Home Addition?
A home addition is a construction project that expands your existing living space. It can be a single-room extension, a second-story addition, or even an attached garage. Home additions increase square footage, improve functionality, and can boost property value when planned correctly.
How Much Does a Home Addition Cost?
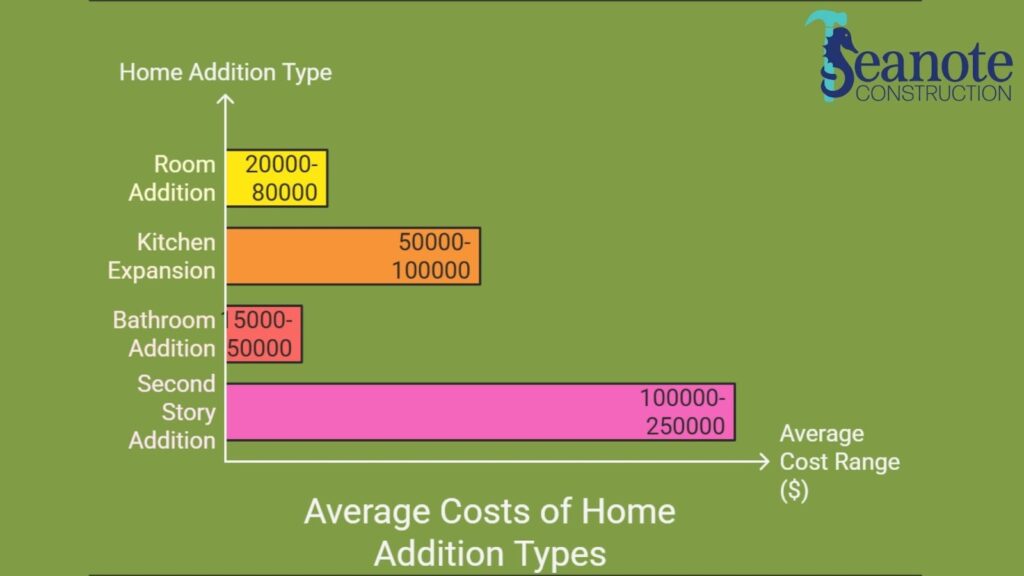
The cost of a home addition depends on factors like size, materials, and labor. According to Bankrate, the average home addition in 2025 costs between $20,000 to $80,000, with prices increasing for larger projects.
| Home Addition Type | Average Cost | Cost per Square Foot |
| Room Addition | $20,000 – $80,000 | $100 – $200 |
| Kitchen Expansion | $50,000 – $100,000 | $150 – $300 |
| Bathroom Addition | $15,000 – $50,000 | $200 – $300 |
| Second Story Addition | $100,000 – $250,000+ | $150 – $250 |
What Factors Influence the Cost of a Home Addition?
The cost of a home addition depends on several key factors. Knowing what drives expenses helps you plan and avoid surprises.
Size and Scope
Larger additions cost more due to increased materials and labor. A basic bedroom addition is cheaper than an expanded kitchen with custom finishes.
Materials and Finishes
High-end materials like quartz countertops or custom cabinetry raise costs. Standard options lower expenses without sacrificing quality.
Labor and Permits
Labor is one of the biggest costs in any home addition. Skilled trades like electricians and plumbers charge varying rates, and permitting fees add another layer of expense.
Location
Urban areas typically have higher labor and material costs than rural regions. Climate can also affect material needs and pricing.
Site Preparation and Cleanup
Demolition, grading, and post-construction cleanup add expenses. Unexpected site issues, like tree removal or foundation work, can increase costs.
Building Up vs. Out
Adding a second story is often cheaper if the foundation can support it. Expanding outward requires new foundation work, increasing costs.
How Can I Assess My Financial Readiness for a Home Addition?
Before choosing a financing option, you need to know where you stand financially. Lenders look at your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and home equity to determine your borrowing power.
How Does My Credit Score Affect Financing Options?
A higher credit score gets you lower interest rates and better loan terms. Most lenders prefer a score of 620 or higher for home equity loans and 700+ for the best HELOC (Home Equity Line Of Credit) rates. Check your score through a free credit report and correct any errors before applying.
What Is Debt-to-Income Ratio and Why Is It Important?
Your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio measures how much of your income goes toward paying debts. Lenders typically want a DTI below 43%, but the lower, the better. Calculate it by dividing total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income. Paying down existing debt improves your ratio and increases loan approval chances.
What is Home Equity and How Do I Calculate It?
A home equity loan is a lump sum borrowed against your home’s equity. It has a fixed interest rate and predictable monthly payments, making it ideal for homeowners who want a structured repayment plan.
The Wall Street Journal reports that the average home equity loan interest rate is 8.37% as of March 2025, with rates ranging between 8.04% and 9.24%. Borrowers with strong equity and credit history secure the best rates.
Calculate it using:
Home Value – Mortgage Balance = Home Equity
6 Ways to Finance Your Home Addition
Below are some of the most effective ways to fund your home expansion project:
1. Use Your Home’s Equity
If you’ve built up equity in your home, you can tap into it through either a Home Equity Loan or a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC).
- Home Equity Loan: A lump-sum loan with a fixed interest rate, ideal if you know exactly how much your addition will cost.
- HELOC: A flexible credit line that lets you draw funds as needed, great for phased or evolving renovation projects.
Pros:
- Typically lower interest rates than unsecured loans
- May offer tax-deductible interest (consult a tax advisor)
Cons:
- Your home is used as collateral
- Requires sufficient existing equity
2. Cash-Out Refinance
This option involves refinancing your mortgage for a higher amount than you currently owe and taking the difference as cash to pay for the renovation.
Pros:
- Consolidates your mortgage and renovation financing into a single loan
- Potential for better interest rates if current rates are lower than your original mortgage
Cons:
- Higher closing costs
- Extends or restarts your mortgage term
3. Personal (Unsecured) Loans
Personal loans don’t require collateral, making them a convenient option, especially if you don’t have much equity or don’t want to touch your mortgage.
Pros:
- No home equity needed
- Fixed terms and predictable payments
Cons:
- Generally higher interest rates than secured loans
- Smaller loan amounts and shorter repayment periods
4. Construction Loans
Specifically designed for building or major remodeling, construction loans are short-term and based on the projected value of your home after renovations.
Pros:
- Custom-built for large-scale projects
- Funds released in stages as work is completed
Cons:
- Involves a more intricate application and approval process
- May come with higher rates and fees than traditional loans
5. Government-Backed Renovation Loans
Federal programs like the FHA 203(k) and Fannie Mae HomeStyle® loans help homeowners finance both the purchase (or refinance) of a home and renovation costs under a single loan structure.
Pros:
- Low down payments
- More lenient credit requirements
Cons:
- Slower approval timelines
- Must meet specific property and project requirements
6. Local or Zero-Interest Loan Programs
Some cities, counties, and nonprofit organizations offer low or even zero-interest loans for qualifying homeowners doing specific types of home improvements.
Pros:
- Extremely affordable financing
- Supports energy efficiency or safety upgrades
Cons:
- Availability varies by location
- Funding caps and usage restrictions apply
How Do I Create a Budget and Manage Costs for My Home Addition?

Break down all potential costs to see the full picture. Include:
- Materials – Lumber, flooring, fixtures, paint
- Labor – Contractor fees, electricians, plumbers
- Permits & Inspections – Required by local building codes
- Unexpected Expenses – Factor in 10-20% extra for surprises
A simple spreadsheet or a budgeting app can help track costs and prevent overspending.
How Can I Monitor Expenses During Construction?
Unexpected costs can add up fast. Stay on track by:
- Getting multiple contractor quotes to compare pricing
- Requesting itemized invoices to see exactly what you’re paying for
- Tracking costs weekly to catch overspending early
Cost-Saving Tips for a Home Addition
A home addition doesn’t have to be expensive. Strategic planning and smart choices can cut costs without sacrificing quality.
Choosing Cost-Effective Materials
Budget-friendly materials can provide the same durability and style as high-end options.
- Engineered wood costs less than hardwood flooring.
- Quartz is a durable, affordable alternative to granite.
- Pre-fabricated cabinets save thousands compared to custom-built options.
Hiring the Right Contractors
Getting multiple bids makes sure you get the best price. Contractors charge differently based on demand, experience, and materials used.
- Compare at least three estimates before making a decision.
- Check reviews and ask for references to avoid unreliable contractors.
- Negotiate pricing, especially if you’re flexible on scheduling.
Timing the Project for Lower Costs
Contractors are busiest in spring and summer, which drives up prices. Scheduling work in fall or winter can lower labor and material costs by 10-20%.
What Permits and Regulations Do I Need to Consider?
Skipping permits or ignoring regulations can lead to fines, delays, or even having to tear down work. Understanding local building codes allows your home addition to be safe and legally compliant.
Adhering to Local Building Codes
Every city has building codes that dictate construction standards, covering:
- Structural integrity (foundation, framing, roofing)
- Electrical and plumbing systems
- Fire safety and energy efficiency
Non-compliance can cause issues when selling your home or filing insurance claims.
Obtaining the Necessary Permits
Permits vary by location. Common permits include:
- Building permits – Required for structural changes, expansions, and new rooms.
- Electrical and plumbing permits – Needed when adding wiring, outlets, pipes, or fixtures.
- Zoning approval – Makes sure the addition follows setback and land-use regulations.
Permits are obtained through the local building department. Applications typically require project plans and may take a few weeks for approval.
Compliance During Construction
City inspectors verify that work meets safety codes at key stages of construction. Failing inspections can mean costly fixes or project delays.
- Hire licensed contractors familiar with local requirements.
- Schedule inspections as required to avoid last-minute issues.
- Keep copies of permits and inspection approvals for future reference.
Following the right procedures from the start prevents legal trouble down the line.
Make Your Home Addition a Reality, Without the Guesswork

Financing a home addition doesn’t have to be stressful. With the right plan, a clear budget, and smart financing, you can expand your space without unexpected costs or complications. The key is working with a team that’s upfront, organized, and always has your back.
At Seanote Construction, we take on tough projects, communicate clearly, and stand behind our work, because we believe in doing things the right way. If you’re ready to start your home addition with a team that tells it like it is, reach out today. Let’s talk about your project and build something that lasts.

